Off-grid solar systems, also known as stand-alone power systems (SAPS), are among the most common types of solar power systems. It works by generating electric current from the solar cells and using it to charge a solar battery with the help of a voltage regulator. An inverter then converts this electricity into usable energy that can power homes and other business appliances. It is possible to operate electrical devices on solar energy even at night or with limited sun exposure by storing electricity in a solar battery.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar Power System
i) Solar panels or photovoltaic cells
A solar panel is the first and most important part of the solar production system. The precise size and the energy production capacity of the individual solar panel array will depend on several things, including:
- Usable space of the roof;
- The amount of available sunlight in the area;
- Energy consumption requirements.
ii) Solar batteries
A solar battery is a device that you can connect with your solar power system to save excess energy generated by the solar cells. You can then use the stored electricity to power your house when your solar panels aren’t producing enough electricity, such as at night, on cloudy days, or during power outages. People can either use a single battery or a battery bank, depending on their energy needs.
The primary purpose of a solar battery is to help you get the maximum benefit from the solar energy you are generating. If you don’t have battery storage, any excess electricity generated by solar panels is fed into the grid, which means you’re producing power and distributing it to others without fully utilizing the electricity generated by your panels.
iii) Solar inverters
Solar power systems require a solar inverter — also known as a solar converter or a PV inverter — to convert the direct current (DC) collected by solar panel arrays into alternating current (AC) for powering most common household appliances and electronics. You can also use a stand-alone inverter for an off-grid system.
iv) Solar charge regulators
A charge controller, also known as a charge regulator, is a voltage or current regulator to prevent batteries from overcharging. It regulates the current and voltage going to the battery from the solar panels. Most “12-volts” solar panels produce around 16 to 20 volts. Therefore, you must include charge regulators in a power-generating circuit to avoid potential electrical hazards. Also, most batteries require between 14 and 14.5 volts to charge completely.
v) Alternative power source
It may be worthwhile to consider an alternative energy source as a backup to the solar system. This is particularly important in the winter when solar output is at its lowest. Many people who use off-grid systems connect them with generators to supply electricity to their homes.
6 Easy Steps to Build an Off-Grid Solar System
Do you want to build your off-grid solar system? Here are the six simple steps to help you get started.
Step 1: Determine how much power you will need
The most crucial point to consider when building an off-grid solar system is how much energy you need and how your electricity usage varies throughout the day and year. Renewable energy sources are inherently variable; therefore, knowing the daily and yearly patterns of your family’s energy usage is critical to designing an efficient solar power system.
Please note that this is the first step in installing an off-grid solar system, and getting it right will significantly impact the rest of the process.
Step 2: Selecting the best location for installing your panel
The next step is to find the ideal location for the solar panels that get the maximum sunlight. The top of the house isn’t always the best location for an off-grid solar array. You can double the efficiency of your solar panels by avoiding excessive shady sites while also ensuring proper access and passive cooling mechanisms for your solar cells.
Step 3: Ordering the appropriate solar system components
Once you’ve decided the location of the solar panels, you’ll be able to estimate the power potential of your site. After that, you will need to select and order the necessary components to mount your solar panel system. You have several options to consider at this point, including:
- The number and precise size of your solar panels
- The type and size of your voltage regulators (MPPT vs. PWM, etc.)
- Consider your battery bank’s capacity and the type of battery you’re using.
- Choosing the overall power output of each leg and which loads should be DC or AC.
- The rating of your converter or inverter, if any.
Step 4: Creating your solar battery house or compartment
After you’ve ordered the solar components, you would be ready to construct your battery house, which could be a room in your existing home, a separate shed, or a part of your garage. Batteries typically take up a lot of space. Therefore, they must be kept out of the reach of children or animals who might injure themselves by touching the contacts or accidentally damaging the battery, releasing the acids inside.
Furthermore, most batteries require temperature regulators and do not function well in cold temperatures. Suppose you purchase less expensive unsealed batteries. In that situation, you will need to add ventilation to your battery house to prevent the accumulation of explosive hydrogen gas, which these batteries emit in small amounts when charging. It’s always preferable to invest in high-quality solar systems that will help you save a considerable amount of money on other expenses. It’s important because most high-quality solar systems include charge controllers and inverters in the battery room, as well as safety shutoffs, fuses, and breakers, all of which can cost you extra dollars if you go with low-cost solar panels.
Step 5: Installing solar cells
Finally, it’s time to construct the panel support and mount the solar array. Solar cells are far more efficient when they have direct sunlight exposure, and they last longer when they are rigid and well-cooled. A proper solar support network can be built in multiple ways, depending on the materials available and the skills you use. We recommend constructing a south-facing A-frame structure out of metal or wood with the ability to manually adjust the angles of your panels during the winter and summer to boost your power output by up to 45 percent with no additional cost.
You could even go one step further and build your one- or two-axis tracking system. Check out FreeSolarPowerQuotes.com for more information on how to install solar panels.
Step 6: Wiring up for a small off-grid solar system
Now that the panels are in place, it’s time to wire the whole system together. This step does not seem to be complicated. Going off the grid with a permaculture homestead, country cabin, or boondocking RV enables you to have a much simpler electrical system than gird tie systems.
Going off the grid means you have the option of installing an all-DC system, which is both simple and effective. But if you want to connect your solar system to the grid power supply, you will most likely be required to hire a licensed electrician to wire it into the primary system. Also, you’ll need additional hardware from your utility company to make your energy system work with the main power line.
How much does an off-grid solar power system cost?
Off-grid systems can cost anywhere from $50 (for a tablet or phone charger) to tens of thousands of dollars. That’s because an off-grid solar system has a wide range of applications.
If we specifically mention off-grid solar kits that can power an entire home, in which case the costs range from $12,000 to $50,000.
The figure below shows popular off-grid kits for various end-use requirements and can help you estimate their costs.
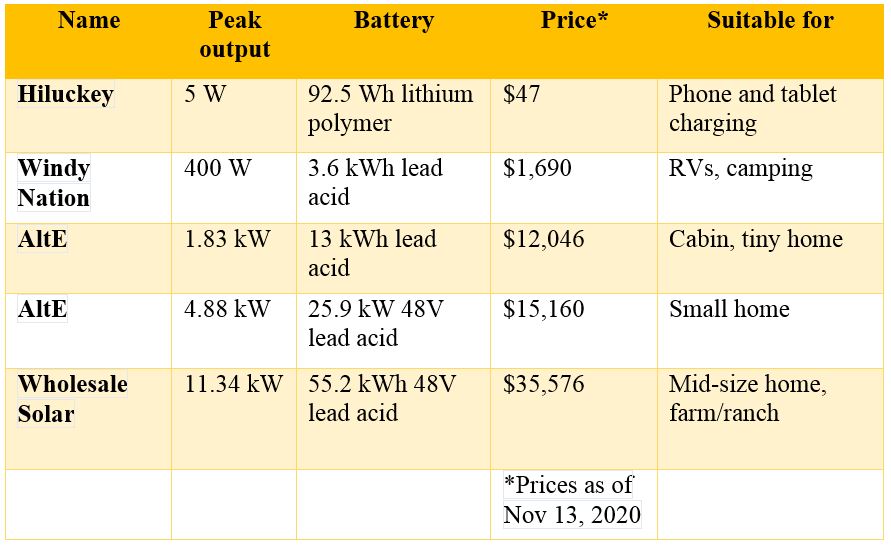
Please note that the costs listed are only for off-grid solar panel kits, i.e., just the equipment. There will be additional costs for labor work if you hire a professional solar company to install your panels. But with DIY, you will only be responsible for covering the costs of permits and tool requirements.
The impact of battery types on costs
Except for the Hiluckey phone charger, all the solar kits listed above include AGM lead-acid batteries. Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are a top pick for off-grid solar power systems because they are convenient, need little maintenance, and are relatively inexpensive when compared to lithium batteries.
Where can I buy an off-grid solar system kit?
The purchasing process for an off-grid system will vary depending on the size of the solar system you want.
Best place to find a full-service solar company
If you are looking for solar installers that can handle the entire installation process for your off-grid solar system, from system design and pricing to installation, permitting, and monitoring, then check out the FreeSolarPowerQuote. It will help you find the best local solar power companies in your area based on customer reviews.
Best place to buy medium and large-size off-grid system kits
Suppose you’re a do-it-yourselfer (DIYer) looking to power an entire solar structure, such as a shed, house, cabin, or even a ranch or farm. In that case, you’ll consider purchasing solar equipment from a reputable solar equipment distributor. Both Unbound Solar (previously known as Wholesale Solar) and the altE Store offer excellent plans and support with their kits.
Best for small and transportable off-grid solar systems
People who travel frequently or use an RV have several options for buying portable solar systems, including Amazon, Home Depot, Best Buy, and others. The famous United States brands that provide the best mobile off-grid solar systems are Grape Solar and Renogy.
Nonetheless, many companies are now available that offers off-grid solar power system at significantly lower prices.
Is an off-grid solar power system suitable for your needs?
The off-grid solar system is the most suitable energy source when it is difficult (or impossible) to access the primary power supply. It’s hard to imagine, say, a traveler or camping enthusiast who forgo solar system in favor of a generator, which is heavy, noisy, and requires costly fuel.
It is also typically the best option for those committed to living a low-carbon, eco-friendly lifestyle. Other renewable energy resources, such as hydro and wind power, are more expensive and require access to a constant supply of water and wind.
On the other hand, off-grid living is not the right option for homeowners who live in or near the city. That’s because off-grid systems installed in homes are more expensive and rarely yield savings over the main power supply. Furthermore, off-grid solar systems are not connected to the utility grid, making it difficult to provide electricity in certain circumstances such as battery failure, network damage, and other problems.
If you’re looking for a way to save money, grid-tied solar systems are the way to go. These are environment-friendly, convenient sources of energy and can save up to $100,000 or more in some regions. And having a connection with the utility grid means that you have constant access to all of the power you need. You can get more information about grid-tied solar systems here.
FAQS
How many solar panels are required to power an off-grid home?
A typical off-grid solar system in the United States is 5 kW, which means you’ll need 20 solar cells at 250-watt or 50 smaller 100-watt panels. Also, it depends on your energy needs and the amount of sunlight that reaches the panels, which in turn power your house.
What are the components of off-grid solar systems?
The following are the components of off-grid solar:
- Photovoltaic cells or solar panels (mono or poly)
- Voltage regulator or charge controller (PWM or MPPT)
- Battery bank (lead-acid, lithium, or other)
- Disconnects and fuses
- Inverter (pure sine wave)
- Copper wire
- Miscellaneous connectors
How does the solar system impact my property values?
According to studies, homes with solar power systems sell at better prices than homes without them. Nevertheless, your property value only increases if you own your solar panel system instead of leasing it.
In most regions of the country, going solar will increase the value of your home more than a kitchen renovation.
How much will off-grid solar panel maintenance cost?
Solar panel systems are made of rigid tempered glass and require very little maintenance. Furthermore, you don’t even need to clean your panels on a day-to-day basis. Most equipment manufacturers provide product warranties, though the terms and conditions vary by company.

